What Best Describes Secondary Protein Structure
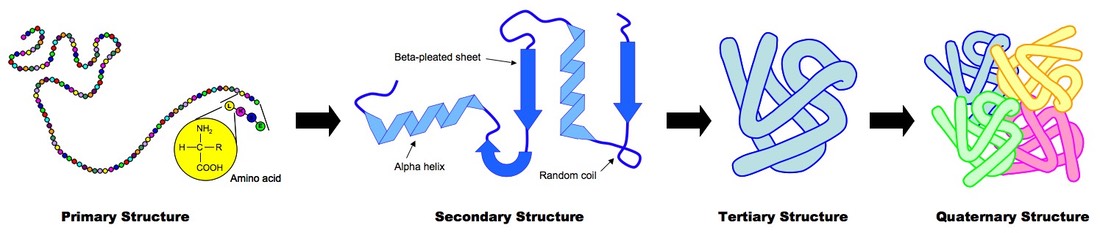
The three dimensional structure of a protein due to the spatial arrangement of the side chains of the amino acids that make up the polypeptide and the bonds formed in between them is termed the. Secondary structure of protein refers to local folded structures that form within a polypeptide due to interactions between atoms of the backbone.
The Structural Level Of A Protein Least Affected At Level
The order in which amino acids exist in a protein is known as its primary sequence.

. Secondary structure of a protein is formed by Interaction of its QUESTION 8 contain fatty acids and glycerol joined together by ester bonds. The most common type of secondary structure in proteins is the α-helix. The helical structure forms due to the presence of the turns in the polypeptide chain and different helical structure are identified on the basis of the number of.
Biology questions and answers. The primary structure is defined as the sequence of amino acids that compose a polypeptide chain. QUESTION 9 If a monosaccharide has a single carbonyl group situated between two carbon atoms which of the following best describes that monosaccharides.
Questioned Answered Which of the following describes the secondary structure of a protein. Alpha helix and beta sheets are the major secondary structures of a protein. A The secondary structure of a protein refers to the sequence of amino acids in its polypeptide chain.
The secondary structure of a protein depends on backbone interactions and is also probably unaffected. Protein structure has 3 levels. The second type of secondary structure in proteins is the beta β pleated sheet.
The sequence of the various amino acids that make up a polypeptide chain B. The total number of amino acids that make up a polypeptide chain and its overall resulting length. A small grouping of secondary structures.
Alpha helix and beta pleated sheet. Group of answer choices complex 3-dimensional folding pattern of a polypeptide helix or pleated sheet pattern of a polypeptide ordered sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide interaction of more than one polypeptide chain. This is what we call the tertiary structure of proteins.
What is the secondary structure of a protein Other answers discuss alpha helix and beta sheets so Ill mention other levels. Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary. There are different types of helical structure were observed in the proteins but the most common is the α-helix.
Regions of a protein that have no specific function. Nucleotide Structure Phosphate group 5-carbon sugar and a nitrogenous base. This structure appears to be folded or pleated and is held together by.
The prediction was confirmed when the first three-dimensional structure of a protein myoglobin by Max Perutz and John Kendrew was determined by X-ray crystallography. Answer 1 of 5. Proteins are divided into 20 distinct amino acids.
Secondary structure elements typically spontaneously form as an intermediate before the protein folds into its three dimensional tertiary structure. There are two types of secondary structures observed in proteins. Which of the following is the Secondary structure of protein describes Tertiary structure and quanternary structure.
After the amino acids form bonds secondary structure and shapes like helices and sheets the structure can coil or fold at random. It is commonly occurring enough to have an identified structure. The backbones regular repeating folding patterns are referred to as a proteins secondary structure.
What best describes the main determinant of the secondary structure of a protein. The term secondary structure refers to the interaction of the hydrogen bond donor and acceptor residues of the repeating peptide unit. Up to 10 cash back A protein motif aka supersecondary structure is a defined arrangement of secondary structures within a protein.
A linker region between two α-helical structures. The most common secondary structures are alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter.
The global 3D shape of the entire peptide chain. Secondary protein structure is the general 3-dimensional form of local segments of a protein. Long polypeptide chains fold or coil to form secondary structure.
I α helix- In this the chain is coiled spirally generally in the right handed manner. The primary structure of a protein is its amino acid sequence. A section of a protein structure sufficient to perform a particular chemical or physical task.
If this structure is disrupted or disturbed a protein is said to be denatured which means it is chemically affected and its structure is distorted. A sequence of amino acids B alpha helix and beta sheet C two or more proteins together D interactions between the amino acid side chains. This structure resembles a coiled spring and is secured by hydrogen bonding in the polypeptide chain.
Introduction to proteins and amino acids. Match letters pls athe 3D arrangement of small localized regions of amino acids into structures called alpha helix or beta-pleated sheet b. B The secondary structure of a protein is the folded structure alpha-helix or beta-sheet formed by additional bonds that are formed in the polypeptide chain.
With respect to proteins which of the following statements BEST describes secondary structure of proteins. Overview of protein structure. Introduction to amino acids.
The secondary structure of a protein is formed due to hydrogen bonding present amino acid molecules. The helical structure in the protein is one of the common secondary structure exist. These secondary structures are produced and maintained by hydrogen bonding Two types of secondary structures are.
The two most important secondary structures of proteins the alpha helix and the beta sheet were predicted by. The original and substitute amino acid both have a negative charge and can both form an ionic bond with a positively charge amino acid so contributions to quaternary and tertiary structure which are dependent on side-chain interactions are most likely unaffected. An example would be the beta-alpha-beta loop.
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional form of local segments of proteinsThe two most common secondary structural elements are alpha helices and beta sheets though beta turns and omega loops occur as well. Orders of protein structure. Linus Pauling was the first to predict the existence of α-helices.
One type is the alpha α helix structure.
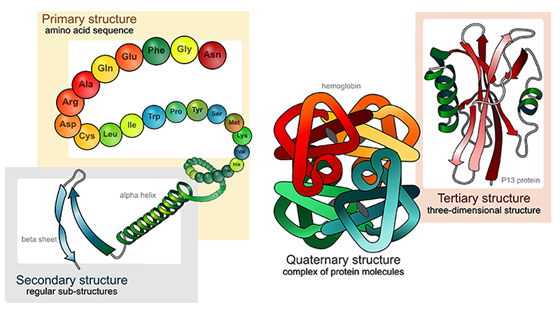
Four Types Of Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Structures

Protein Secondary Structure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
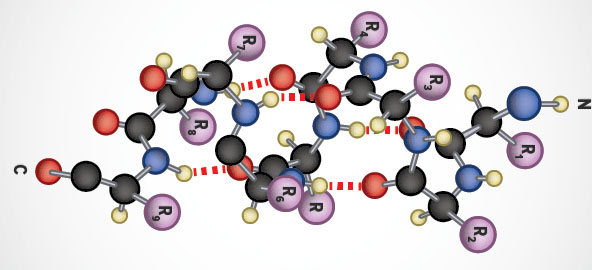
Protein Structure And Analysis The Medical Biochemistry Page
Protein Structure Introduction To Chemistry

Cell Membranes Function Structure And Composition Cell Membrane Cell Membrane Plasma Membrane Cell Biology
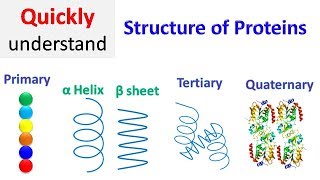
Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Youtube

David Chalk Teacherchalky1 Twitter Middle School Science Activities Teaching Biology Medical Student Study

Mitosis And Cytokinesis An In Depth Lecture About The Phases Of Mitosis Great For Higher Life Science Lessons High School Science High School Science Teacher
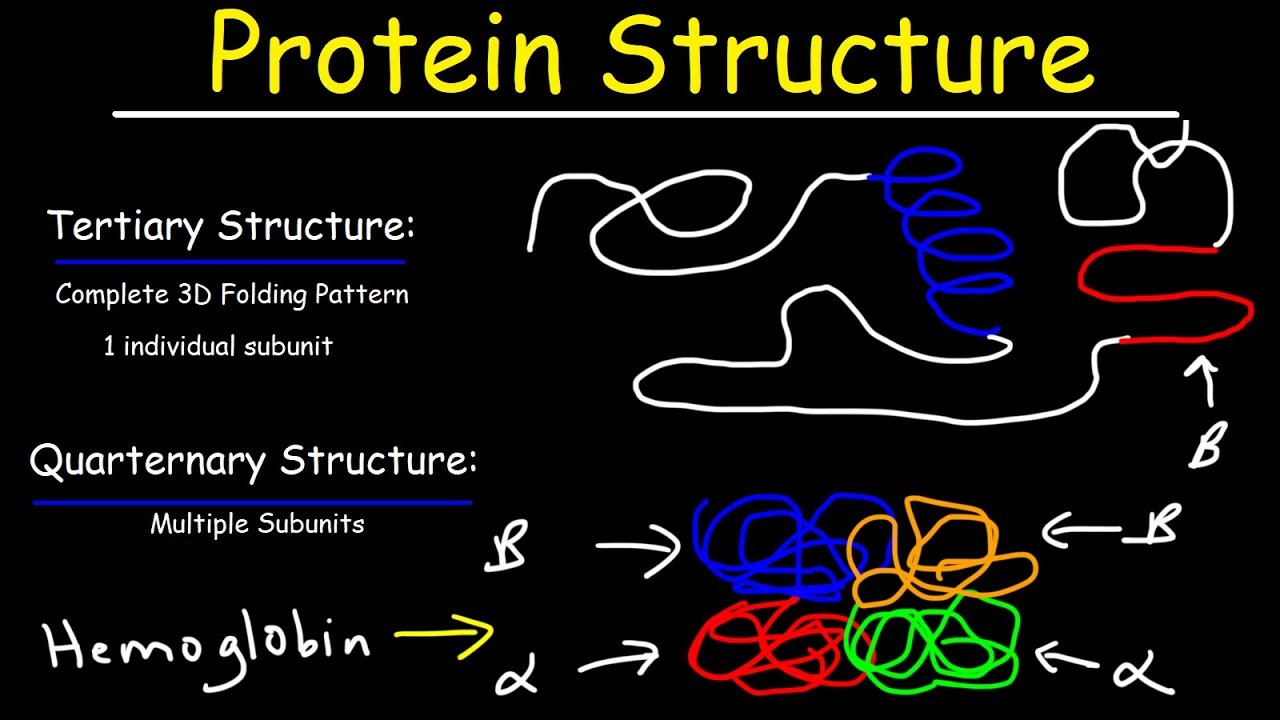
Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quarternary Biology Youtube

Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Youtube

Mla Ce Course Manual Molecular Biology Information Resources Genetics Review 3 D Protein Structures

Levels Of Protein Organization

Levels Of Protein Organization

A Primer For Protein Structure Walk In The Forest
Protein Structure Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Different Organisms Dna Organs Blood Hormone Used

Cellular Organelles Teaching Cells Cell Transport Cell Membrane Transport

Enzymes Doodle Docs Biology Worksheet Biology Activity Enzymes Biology

Comments
Post a Comment